Introduction
Definition: Shell
A shell is a text-based program for interacting with an operating system.
On a very general level, what a shell does is straight-forward: it takes text commands, processes them, performs the actions they outline and then handles any resulting text output.
There are many different shells you can install and use. Most, however, are only available on particular operating systems. For example, the Bourne-Again Shell (bash) is the most commonly used shell on Linux, while PowerShell dominates the world of Windows.
Every shell comes with its own scripting language which is used to write commands. These languages can vary significantly in functionality and complexity. Some only allow you to launch other programs, while others are capable of performing many other complex tasks.
Interactive Mode
Definition: Interactive Mode
When a shell runs in interactive mode, it obtains its input directly from you. You are personally responsible for typing in each command and then sending it to the shell (usually by pressing Enter).
In interactive mode, most shells usually have the option to display useful information at the beginning of each line in a piece of text called a prompt.
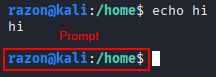
Depending on the shell, the prompt can be configured to display many things, such as the current user, directory, time, hostname, etc.
Non-Interactive Mode
When a shell runs in non-interactive mode, it obtains its input from somewhere other than you. Most commonly, it reads the commands from a file, but it can also source them from a network connection, for example.